Eat Smart, Move More, Weigh Less can help your employees decrease their risk and costs associated with obesity.
Obesity and Obesity-related Conditions
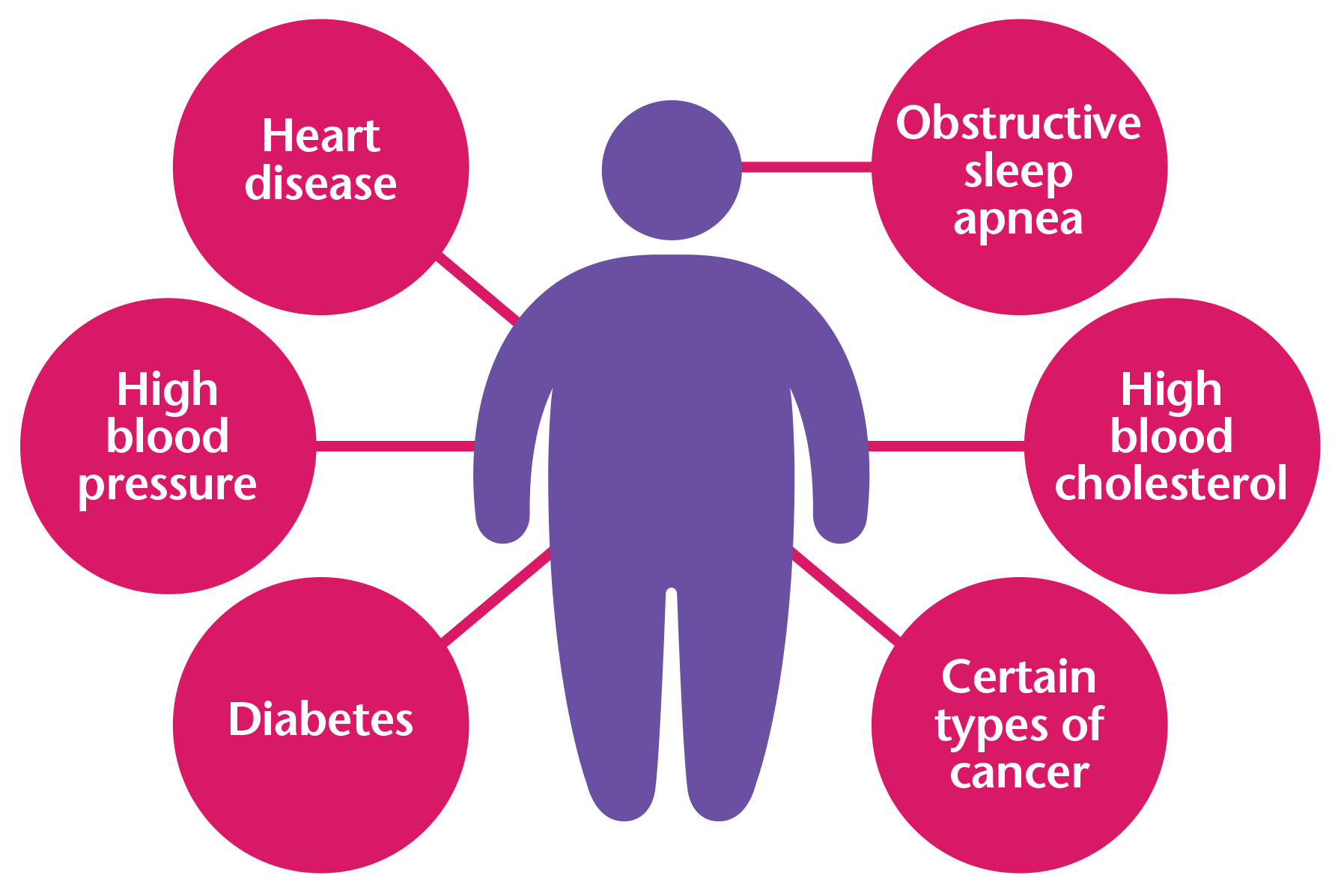
Obesity is linked to the leading causes of preventable death1.
Obesity puts an individual at risk for developing2:
Obesity and Diabetes
New cases of diabetes have increased over the past several years.
The average medical cost for a person in the United States with diabetes is 2.3 times higher – equating to about $9,600 annually – compared to a person without diabetes3,4.

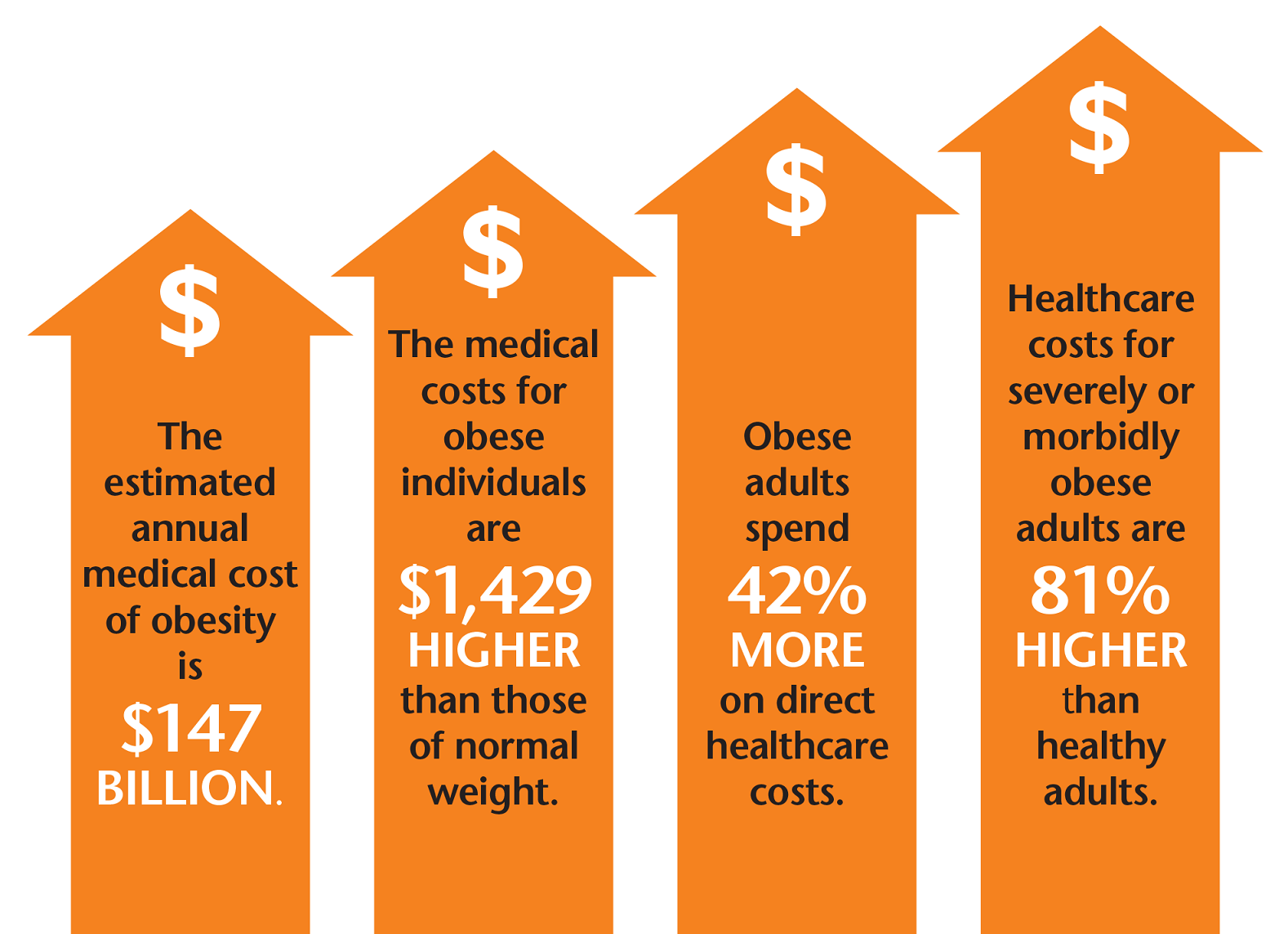
Obesity Increases Medical Costs
Obesity is associated with job absenteeism, costing over $13 billion in the United States annually7.
Obesity Increases Employer Costs
Obesity is associated with job absenteeism, costing approximately $4.3 billion in the United States annually7.
To learn more about improving the health of your employees, request a demo:
Resources:
- Obesity and overweight fact sheet. World Health Organization. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight. Updated June 9, 2021.
- Overweight and Obesity. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/overweight-and-obesity. Updated February 24, 2022.
- Statistics about Diabetes. American Diabetes Association. www.diabetes.org/diabetes-basics/statistics. Updated July 28, 2022.
- American Diabetes Association. Economic costs of diabetes in the U.S. in 2017. Diabetes Care. 2018;41(5):917-928. https://doi.org/10.2337/dci18-0007
- Van den Broek-Altenburg E, Atherly A, Holladay E. Changes in healthcare spending attributable to obesity: Payer-and service-specific estimates. BMC Public Health. 2022;22:962. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-022-13176-y
- Cawley J, Biener A, Meyerhoefer C, Ding Y, Zvenyach T, Smolarz BG, Ramasamy A. Direct medical costs of obesity in the United States and the most populous states. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2021;27(3):354-366. doi:10.18553/jmcp.2021.20410
- Cawley J, Biener A, Meyerhoefer C, Ding Y, Zvenyach T, Smolarz BG, Ramasamy A. Job absenteeism costs of obesity in the United States: national and state-level estimates. J Occup Environ Med. 2021;63(7):565-573. doi: 10.1097/JOM.0000000000002198
